Protecting music data privacy has become a top concern as over 90 percent of american music platforms now rely on advanced analytics powered by user data. With personal listening habits and creative fingerprints at stake, both listeners and artists face real risks from misuse or unauthorized access. This article explains the crucial facts every professional needs to understand about the evolving challenges surrounding music data privacy, helping you navigate this rapidly changing digital landscape with confidence.
Table of Contents
- Defining Music Data Privacy In Analytics
- Types Of Music Data And Privacy Risks
- Music Privacy Laws And Global Frameworks
- Anonymization Methods In Playlist Analysis
- Industry Obligations And Compliance Requirements
Key Takeaways
| Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Music Data Privacy | Protecting sensitive information in music analytics is essential due to increasing reliance on AI and data collection techniques. Organizations must implement cryptographic protection to maintain artist and listener privacy. |
| Privacy Risks | Music data includes listener profiles and creative identifiers, posing various privacy risks that require robust anonymization techniques and clear consent protocols. |
| Global Legal Frameworks | Music professionals must navigate an evolving regulatory landscape that balances technological innovation with privacy protections, ensuring compliance with different national laws. |
| Compliance Obligations | Ethical data management is now a fundamental commitment; organizations should be proactive in implementing transparent data policies and conducting regular privacy audits. |
Defining Music Data Privacy in Analytics
Music data privacy represents a critical frontier in modern music technology, where protecting sensitive information while enabling advanced analytics becomes increasingly complex. As generative AI and sophisticated data collection techniques emerge, professionals must understand the nuanced landscape of data protection within music ecosystems.
According to research from arxiv.org, music data privacy involves sophisticated cryptographic approaches designed to safeguard music embeddings from unauthorized access or manipulation. The core challenge lies in preserving individual artist and listener privacy while maintaining the analytical value of collected data. Cryptographic protection has become essential, especially as AI systems increasingly rely on extensive music datasets for training and insights.
Privacy concerns in music analytics extend beyond simple data anonymization. arxiv.org highlights the ethical implications of generative audio models, emphasizing that music data contains intricate personal and creative signatures that require robust protection mechanisms. Key privacy considerations include:
- Protecting individual artist identities
- Preventing unauthorized data reuse
- Maintaining listener confidentiality
- Securing proprietary musical embeddings
- Ensuring transparent data usage policies
For music industry professionals, understanding these privacy dynamics is not just a technical requirement but a strategic imperative. By implementing sophisticated data protection strategies, organizations can build trust, comply with emerging regulations, and leverage advanced analytics responsibly.
With the Types of Music Industry Data guide, professionals can dive deeper into understanding the complex landscape of music data management and privacy protection strategies.
Types of Music Data and Privacy Risks
Music data encompasses a complex ecosystem of sensitive information that ranges from personal listening habits to intricate creative identifiers. Understanding the various types of music data and their associated privacy risks is crucial for professionals navigating the modern digital music landscape.
arxiv.org reveals a critical dimension of music data privacy through its analysis of dataset representation, highlighting how data collection practices can introduce significant cultural and ethical challenges. The research underscores the systemic biases inherent in music data collection, particularly in the underrepresentation of Global South music genres, which raises profound privacy and representation concerns.
Privacy risks in music data can be categorized into several critical areas:
- Listener Profile Data: Personal listening histories, preferences, and behavioral patterns
- Metadata Insights: Artist information, track details, and genre classifications
- Performance Metrics: Streaming numbers, playlist inclusions, and engagement statistics
- Geolocation Information: Regional listening trends and demographic data
- Creative Fingerprints: Unique musical characteristics and compositional signatures
Listening.com provides additional context by exposing vulnerabilities in music data handling, particularly the risks of unauthorized recordings and potential data breaches. These risks extend beyond simple data collection, encompassing complex ethical considerations about ownership, consent, and data utilization.

Professionals can mitigate these risks by implementing robust data anonymization techniques, establishing clear consent protocols, and developing transparent data usage policies. For a comprehensive exploration of these nuanced challenges, professionals can refer to the Types of Music Analytics guide, which offers deeper insights into responsible data management strategies in the music industry.
Music Privacy Laws and Global Frameworks
The landscape of music data privacy is rapidly evolving, with global legal frameworks struggling to keep pace with technological advancements in digital music collection and analysis. Music industry professionals must navigate an increasingly complex regulatory environment that balances technological innovation with fundamental privacy protections.
Link.springer.com provides critical insights into how national cultures and privacy protection laws directly impact AI innovation and data management strategies. The research highlights the intricate relationship between legal frameworks and technological development, revealing that privacy regulations are not uniform but deeply contextual across different global jurisdictions.
Key global privacy frameworks for music data typically address several critical dimensions:
- Personal Data Protection: Regulations governing individual listener information
- Consent Mechanisms: Requirements for explicit user agreements
- Data Retention Policies: Rules about storage and deletion of musical data
- Cross-Border Data Transfers: International guidelines for sharing music analytics
- Algorithmic Transparency: Mandates for explaining data-driven decisions
Wikipedia offers additional context through its examination of regulatory approaches, such as the UK's Online Safety Act 2023, which demonstrates how governments are increasingly intervening to protect digital user privacy. These legal frameworks represent a sophisticated attempt to balance technological innovation with individual privacy rights.
For music industry professionals seeking to understand these complex regulatory landscapes, the Understanding Music Data Trends guide provides comprehensive insights into navigating these evolving legal challenges while maintaining ethical data practices.
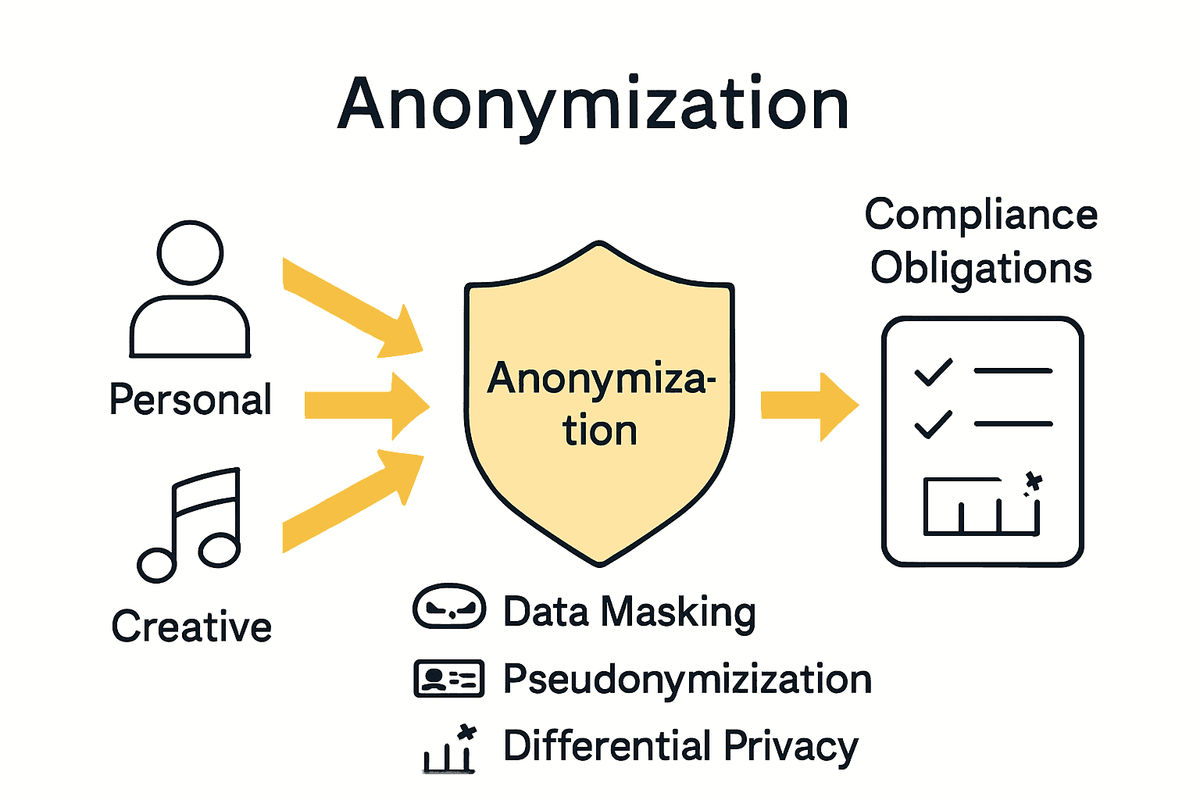
Anonymization Methods in Playlist Analysis
Playlist data anonymization represents a critical challenge in modern music analytics, requiring sophisticated techniques that protect individual user privacy while maintaining the analytical value of collected information. As music platforms accumulate increasingly granular listener data, professionals must develop robust methods to safeguard personal identities and listening patterns.
arxiv.org introduces synthetic data generation as a groundbreaking approach to privacy preservation. This method creates artificial datasets that mimic the statistical characteristics of original playlist data without revealing specific user information. Synthetic data allows music industry professionals to analyze trends, discover insights, and develop strategies while ensuring individual listener anonymity.
Key anonymization strategies for playlist analysis include:
- Generalization: Removing specific identifiers and aggregating data into broader categories
- Pseudonymization: Replacing direct identifiers with randomized unique tokens
- Data Masking: Obscuring sensitive details while retaining overall data structure
- Noise Injection: Adding controlled random variations to prevent individual identification
- Differential Privacy: Implementing mathematical techniques to limit individual data exposure
Wikipedia warns about the mosaic effect, a critical consideration in anonymization where combining seemingly independent anonymized datasets can potentially reveal individual identities. This phenomenon underscores the complexity of truly protecting user privacy in music data analytics.
For music industry professionals seeking deeper insights into these complex privacy strategies, the Private Playlist Analysis guide offers comprehensive strategies for navigating the intricate landscape of data anonymization and protection.
Industry Obligations and Compliance Requirements
The music industry is experiencing a profound transformation in data governance, where compliance has become far more than a legal checkbox—it's a fundamental commitment to ethical data management and user trust. As technological capabilities expand, so do the responsibilities of organizations handling sensitive musical and listener information.
Maripapel.com highlights the critical need for emerging technologies in enhancing data privacy regulations. The research emphasizes that compliance is no longer about merely following rules, but about proactively integrating sophisticated technological solutions that inherently protect user privacy.
Key compliance obligations for music industry professionals include:
- Transparent Data Collection: Clearly communicating what data is collected and why
- User Consent Management: Implementing robust opt-in and opt-out mechanisms
- Data Minimization: Collecting only essential information for specified purposes
- Regular Privacy Audits: Conducting comprehensive assessments of data handling practices
- Cross-Functional Privacy Training: Educating teams about evolving regulatory requirements
Clausius Press provides additional context by addressing the complex challenges in big data privacy protection. The research underscores that compliance is a dynamic process requiring continuous adaptation to technological and regulatory shifts, demanding a proactive and holistic approach to data governance.
Music industry professionals seeking deeper insights into navigating these complex compliance landscapes can explore the Understanding Types of Music Data guide, which offers comprehensive strategies for responsible data management.
Unlock the Power of Music Data Privacy with Music24
The article highlights serious challenges in protecting music data privacy while maintaining analytical value. Professionals face risks like data anonymization pitfalls and compliance hurdles in navigating this complex landscape. Are you ready to turn these challenges into your advantage by adopting advanced, privacy-conscious music analytics?
Discover how Music24.com leverages proprietary access to fully anonymized private playlist data to deliver early insights on emerging artists and micro-trends without compromising listener privacy. With Music24’s unique approach, you get transparent data protection combined with predictive analytics designed to keep you ahead of public metrics. Explore how our platform handles sensitive data responsibly while empowering your A&R and marketing strategies. Start transforming your music discovery today at Music24.com and deepen your understanding with our guides on Types of Music Industry Data and Understanding Music Data Trends. Act now to gain a competitive edge in the evolving music landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is music data privacy?
Music data privacy refers to the protection of sensitive information within music analytics, ensuring that individual artist and listener identities are safeguarded while still allowing for advanced data analysis.
What are the main privacy concerns in music analytics?
Key privacy concerns include protecting individual artist identities, maintaining listener confidentiality, preventing unauthorized data reuse, and ensuring transparent data usage policies.
How can organizations mitigate privacy risks in music data?
Organizations can mitigate privacy risks by implementing robust data anonymization techniques, establishing clear consent protocols, and developing transparent data usage policies to protect individual identities and listening patterns.
What compliance requirements should music industry professionals be aware of?
Music industry professionals should focus on transparent data collection practices, user consent management, data minimization, conducting regular privacy audits, and providing cross-functional privacy training to ensure ethical data management.



