More than 80 percent of music professionals now rely on complex data to guide decisions and spot market trends. With streaming platforms and digital tools reshaping how artists connect with listeners, understanding the main types of music industry data—audio features, symbolic representations, and contextual information—is essential for anyone looking to stay ahead. This guide brings clarity to the different data categories and shows how they fuel innovation and strategy across the music business.
Table of Contents
- Defining Music Industry Data Types
- Distinguishing Public Versus Private Data
- Metadata: Descriptive, Ownership, Performance
- Streaming, Sales, Airplay & Social Metrics
- Analytics Tools And Aggregated Platforms
- Risks, Legal Issues, And Data Compliance
Key Takeaways
| Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Music Data Types | Understanding audio features, symbolic representations, and contextual information is essential for insightful decision-making in the music industry. |
| Public vs. Private Data | Navigating the distinctions between public and private data allows professionals to gain deeper insights and develop competitive strategies. |
| Importance of Metadata | Comprehensive metadata management is crucial for accurate royalty distribution and maximizing revenue potential across music assets. |
| Legal and Compliance Risks | Awareness of legal issues and compliance requirements is vital for ethical data management and maintaining industry standards. |
Defining Music Industry Data Types
Music industry data represents the complex ecosystem of digital and analog information that tracks, measures, and interprets musical performance, audience engagement, and industry dynamics. According to research from arXiv, music data can be comprehensively categorized into three primary domains: audio features, symbolic representations, and contextual information.
These data types serve as critical navigation tools for music industry professionals, enabling detailed insights into artistic trends, listener behaviors, and market movements. Audio features capture the technical characteristics of sound recordings, including frequency, tempo, and acoustic qualities. Symbolic representations translate musical compositions into structured data formats like MIDI or musical notation, allowing algorithmic analysis. Contextual information encompasses metadata surrounding music creation, distribution, and consumption—tracking elements such as streaming statistics, playlist inclusions, geographic listening patterns, and artist demographic details.
Here's a summary comparing the primary music industry data types:
| Data Type | Key Characteristics | Example Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Audio Features | Tempo Frequency Acoustic qualities | Sound analysis Genre detection |
| Symbolic Representations | MIDI data Musical notation Structured files | Composition analysis Algorithmic study |
| Contextual Information | Metadata Streaming stats Artist demographics | Audience insights Trend tracking |
By understanding these nuanced data types, industry experts can make more informed strategic decisions. 7 Top Music Data Sources Every Industry Expert Needs provides deeper insights into how these data categories interconnect and drive music industry innovation. The multifaceted nature of music data allows for sophisticated predictive modeling, artist development strategies, and targeted marketing approaches that go far beyond traditional metrics.
Key characteristics of music industry data types include:
- Quantitative measurement of musical performance
- Detailed listener engagement tracking
- Predictive potential for emerging trends
- Comprehensive representation of musical ecosystems
Professionals leveraging these data types gain unprecedented visibility into the complex, dynamic world of music creation and consumption, transforming raw information into strategic competitive advantage.
Distinguishing Public Versus Private Data
In the music industry, data exists on a complex spectrum ranging from publicly accessible information to highly protected private datasets. According to Copyright Blog, managing music metadata presents significant challenges in navigating the boundaries between public and private data domains.
Public data encompasses information freely available through streaming platforms, social media, charts, and publicly reported metrics. These datasets include total stream counts, chart rankings, publicly shared playlists, and general listener engagement statistics. They represent the visible layer of music consumption that most industry observers can readily access. In contrast, private data represents more nuanced, restricted information that requires specialized access or proprietary collection methods. This includes anonymized user playlist data, detailed listener behavior patterns, micro-genre trends, and granular audience segmentation insights that are not visible through traditional public channels.
The distinction between public and private data is critical for music industry professionals. Types of Music Analytics: Complete Breakdown Guide highlights how private data can provide predictive insights that public metrics cannot capture. Private datasets offer unprecedented advantages by revealing emerging trends before they become mainstream, identifying influential playlist curators, and understanding granular listener preferences that aren't reflected in public metrics.
Key differences between public and private music data include:
- Accessibility level
- Depth of insights
- Predictive potential
- Level of detail and granularity
Professionals who understand and leverage both public and private data can develop more sophisticated strategies for artist development, marketing, and audience engagement, gaining a significant competitive edge in the rapidly evolving music landscape.
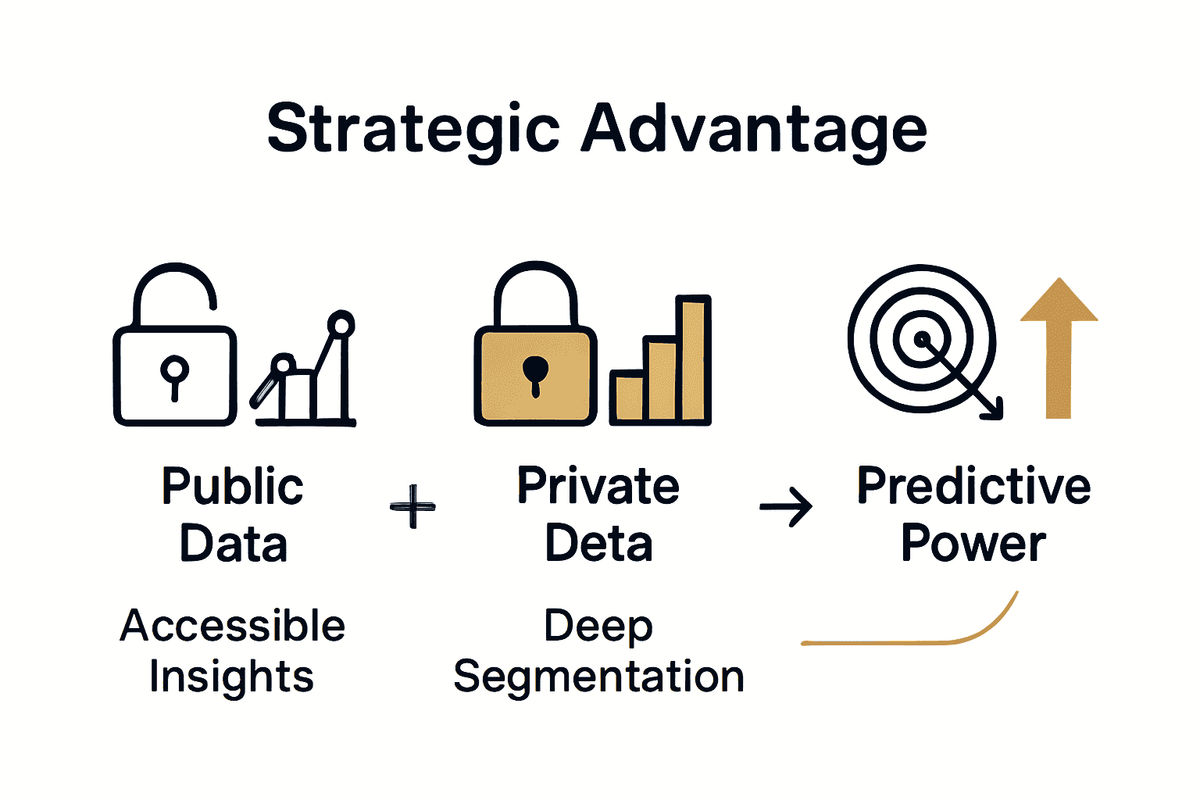
Metadata: Descriptive, Ownership, Performance
Metadata serves as the critical informational backbone of the music industry, providing comprehensive context and essential details about musical works. Copyright Blog highlights the complex challenges surrounding music metadata management, emphasizing its pivotal role in rights administration and economic tracking.
Three primary metadata categories define the music industry's information ecosystem. Descriptive metadata captures the fundamental characteristics of a musical work, including artist name, track title, genre, release date, and album information. Ownership metadata documents the intricate legal landscape, tracking copyright holders, publishing rights, songwriter credits, and licensing agreements. Performance metadata represents the dynamic metrics of music consumption, tracking streaming numbers, geographic listening patterns, playlist inclusions, and revenue generation across various platforms.
Understanding the Role of Metadata in Music Analytics reveals how these metadata types interconnect to provide a holistic view of musical assets. Each category plays a unique role in supporting artists, labels, and industry professionals in making informed strategic decisions, protecting intellectual property, and maximizing revenue potential.
Key implications of comprehensive metadata include:
- Accurate royalty distribution
- Intellectual property protection
- Detailed audience insights
- Enhanced rights management
- Transparent revenue tracking
Professionals who master the nuanced world of metadata gain a significant competitive advantage, transforming raw information into strategic insights that drive innovation across the music ecosystem.

Streaming, Sales, Airplay & Social Metrics
Music industry professionals rely on a complex ecosystem of data metrics to understand artistic performance and audience engagement. According to research from arXiv, machine learning models are increasingly used to analyze factors influencing song popularity by integrating multiple data streams including streaming numbers, sales, airplay, and social media metrics.
Streaming metrics capture digital consumption patterns across platforms like Spotify, Apple Music, and YouTube, tracking total streams, listener demographics, and playlist inclusions. Sales metrics represent traditional and digital purchase data, including digital downloads, physical album sales, and concert ticket revenues. Airplay metrics measure radio and broadcast exposure, tracking radio station plays, time of day, geographic reach, and audience size. Social media metrics analyze digital engagement, including follower counts, share rates, comment sentiment, and viral content performance.
7 Top Music Analytics Metrics Every Industry Pro Must Know reveals how these metrics interconnect to provide a holistic view of an artist's market performance. The true power lies in understanding how these different data points communicate a comprehensive narrative about musical success, audience connection, and potential future trajectory.
Key insights from comprehensive metric analysis include:
- Identifying emerging audience trends
- Predicting potential breakout artists
- Understanding cross-platform performance
- Measuring audience engagement depth
- Tracking revenue generation potential
Professionals who master the nuanced interpretation of these metrics gain unprecedented insights into the dynamic landscape of music consumption, transforming raw data into strategic intelligence that drives artistic and commercial success.
Analytics Tools And Aggregated Platforms
Music industry analytics tools and aggregated platforms represent the technological backbone of modern data-driven music ecosystem insights. According to research from arXiv, these advanced platforms are increasingly sophisticated in their methodologies for collecting, analyzing, and presenting comprehensive music data across multiple dimensions.
Aggregated platforms consolidate data from diverse sources, including streaming services, social media, radio play, and consumer behavior tracking. They transform raw data into actionable intelligence through sophisticated cross-modal retrieval methodologies, as highlighted in arXiv's cross-modal music retrieval research. These platforms typically offer features like comprehensive dashboard visualizations, predictive trend analysis, artist performance tracking, audience segmentation, and real-time metric monitoring.
Understanding Music Analytics Tools in 2025 demonstrates how modern analytics platforms go beyond simple data collection, providing strategic insights that can fundamentally transform music industry decision-making. The most advanced tools integrate machine learning algorithms to predict emerging trends, identify potential breakout artists, and offer granular audience insights that were previously impossible to obtain.
Key capabilities of modern music analytics platforms include:
- Comprehensive data integration
- Predictive trend analysis
- Real-time performance tracking
- Audience segmentation
- Competitive intelligence gathering
Professionals leveraging these sophisticated analytics tools gain unprecedented visibility into the complex, dynamic world of music consumption, transforming raw data into strategic competitive advantage.
Risks, Legal Issues, And Data Compliance
The music industry faces increasingly complex legal challenges surrounding data collection, usage, and intellectual property rights. According to Reuters, recent legal disputes highlight the growing tensions between technological innovation and intellectual property protection, particularly in the realm of artificial intelligence and data usage.
Data compliance has become a critical concern for music industry professionals, encompassing multiple legal domains including copyright protection, personal data privacy, and intellectual property rights. Legal risks emerge from various scenarios such as unauthorized data collection, improper use of artist information, and potential misuse of performance metrics. Retail Tech Innovation Hub emphasizes the increasing regulatory complexity surrounding data management in the entertainment sector, with new compliance requirements challenging traditional approaches to information gathering and utilization.
Navigating these complex legal landscapes requires a comprehensive understanding of emerging regulations and proactive risk management strategies. Professionals must develop robust protocols for data collection, implement stringent consent mechanisms, and maintain transparent processes that respect both technological innovation and individual rights.
Key legal considerations in music industry data management include:
- Obtaining explicit consent for data collection
- Protecting artist and performer intellectual property
- Ensuring transparent data usage policies
- Maintaining robust cybersecurity measures
- Complying with international data protection regulations
Successful music industry professionals recognize that understanding and navigating these legal complexities is not just a regulatory requirement, but a critical component of building trust and maintaining ethical standards in an increasingly data-driven ecosystem.
Unlock the Power of Private Playlist Data to Stay Ahead in the Music Industry
The article clearly highlights how traditional public music data often falls short when it comes to unveiling true listener preferences and predicting emerging trends. If you have felt frustrated by relying only on public streaming stats or social metrics that can delay spotting rising artists and micro-genres, you are not alone. Understanding how private data offers deeper insights into playlist curators, geographic micro-trends, and authentic music discovery patterns is crucial for staying competitive in today’s fast-evolving music landscape.
This is where Music24.com comes in. Our platform exclusively analyzes anonymized private playlists, tapping into millions of unique collections to uncover patterns hidden from public view. This means you gain early access to influential curators and breakout artists long before they appear on popular charts or mainstream social feeds. With powerful predictive analytics and granular geographic trend tracking, Music24.com empowers record labels, artist managers, A&R teams, and marketers to make data-driven decisions with unmatched confidence.
Ready to transform how you identify new talent and track authentic audience engagement?
Discover how leveraging private data can give you a winning edge today.
Visit Music24.com to unlock exclusive insights and start leading the industry with predictive music analytics. Take action now to get ahead of the curve and turn complex data into simple breakthroughs.
Learn more about how Types of Music Analytics: Complete Breakdown Guide connect with private data insights or explore our Understanding Music Analytics Tools in 2025 for a deeper dive into cutting-edge solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main types of music industry data?
Music industry data can be categorized into three primary types: audio features, symbolic representations, and contextual information. Audio features include technical characteristics of sound recordings, symbolic representations involve structured formats like MIDI, and contextual information encompasses metadata related to music creation and consumption.
How does metadata benefit the music industry?
Metadata provides critical context about musical works, including details like artist names, track titles, and copyright information. It plays an essential role in rights administration, accurate royalty distribution, and understanding audience engagement.
What is the difference between public and private music data?
Public music data is freely accessible information available through platforms like streaming services and social media, while private music data is restricted and often provides deeper insights into listener behaviors and emerging trends not visible through public channels.
Why are analytics tools important for the music industry?
Analytics tools are crucial for transforming raw data into actionable insights. They help industry professionals track performance metrics, predict trends, and understand audience engagement, which can inform strategic decision-making and enhance competitive advantage.
Recommended
- Understanding Types of Music Data and Their Importance - Blog - Music24.com
- Understanding Music Data Trends Explained for Industry Leaders - Blog - Music24.com
- 7 Top Music Data Sources Every Industry Expert Needs - Blog - Music24.com
- Types of Music Analytics: Complete Breakdown Guide - Blog - Music24.com